In the financial markets, there are more topics to consider, than it may seem at first glance when you open a trading platform and enter your orders. Various entities in the financial market also have completely different approaches and purposes for operating in the financial market. To correctly understand the entire financial market, you also have to know other participants in the global financial market. Retail traders – These are speculators. You and your friends probably fall into this category, along with many other traders who are reading this article. In the financial market, retail traders operate to invest their capital and their main goal is profit. Retail traders typically trade over the trading platform MetaTrader 4, or through other specific platforms or technology solutions from their broker.
Retail traders in the financial market are trading via a provider, called a broker. Profitability of traders depends on their trading strategy, money management, experiences and also how fair and solid their broker is, and it can vary considerably from 10% to 50%. According to the statistics, the higher the trader’s capital, the higher success rate he is usually able to achieve because he is better at managing risk.
Brokers – Their goal is to provide trading to their clients and provide access to financial markets. For executing their clients’ trades, the broker usually gets a commission. In the world, there are hundreds of brokers with very different approaches to their clients. The fact is that the vast majority of retail traders lose their capital in the financial market, and many brokers put their own profits ahead of creating a profitable trading environment for their clients.
Many brokers therefore, chose dishonest and dirty practices that accelerate the loss of their client’s capital, and they directly benefit from the losses of their clients (a fair broker would only profit from a spread or commission and not from clients’ losses). This is how a lot of all brokerage companies in the world are run.
In any educational materials about brokers and trading, you will read about two types of brokers:
- Dealing desk (market maker) – market makers act like a counterparty for all your trades – and if you have a loss, the market marker earns same amount of money, and vice versa.
- No dealing desk – ECN and STP, which send your trades further into the market for execution.
In fact, there are three types of brokers:
- Dealing desk – market maker, these brokers do not hide the fact that they act like a counterparty to all your trades.
- ECN / STP own or have a contract with only one market maker, which act like a counterparty to all your trades and there is a high conflict of interest as in the first case.
- ECN / STP that are Direct Market Access brokers who actually send all your trades for execution to the interbank market without any conflict of interest.
Traders also often ask us what information about them their broker sees.
Brokers can see all your orders, either at market prices or pending orders, Stop-Loss and Profit- Target (if you type it in the trading platform on the server of your broker). Your broker, of course, can see a complete history of your trades and can tell if you entered a trade manually, by an automated trading system, or over the phone. Your broker does not see your trading strategy or a code of an automated trading system in the trading platform MetaTrader 4. Central banks – the action of central banks and governments are also very important to us. Central banks provide stability of relevant countries by controlling reserves of cash. Central banks are top institutions of banking supervision and determine monetary policy in the country.
The Central Banks perform the following functions:
- Realization of monetary policy
- Supervises the other banks
- Determine exchange rate
- Emit (issues) cash (notes and coins) in circulation
- Maintains an account of the national budget
- Manage foreign reserves
- Commercial banks have their accounts at Central Banks
The main tool of central banks is the interest rate, from which rates by commercial banks are set. By raising and lowering interest rates, the central bank de facto controls the country’s economy and causes severe movements in the financial market.
If we look at the distribution of central banks, depending on who is the owner, we find that there are three groups. Central Bank (CB) in private ownership (an example is – Switzerland or the USA), many other CB are in the hands of the state and the last option is called mixed ownership (eg. Japan).
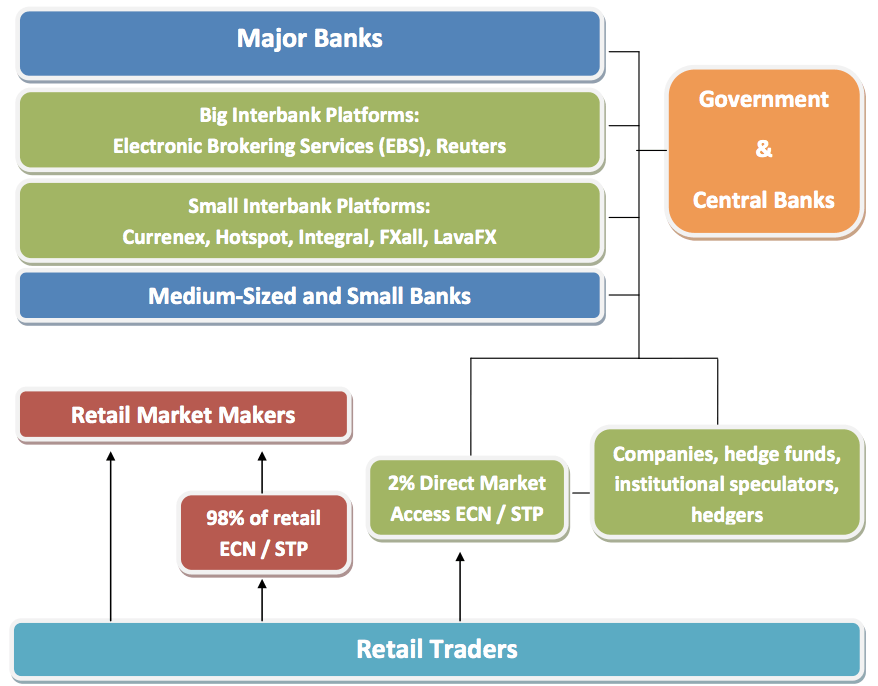
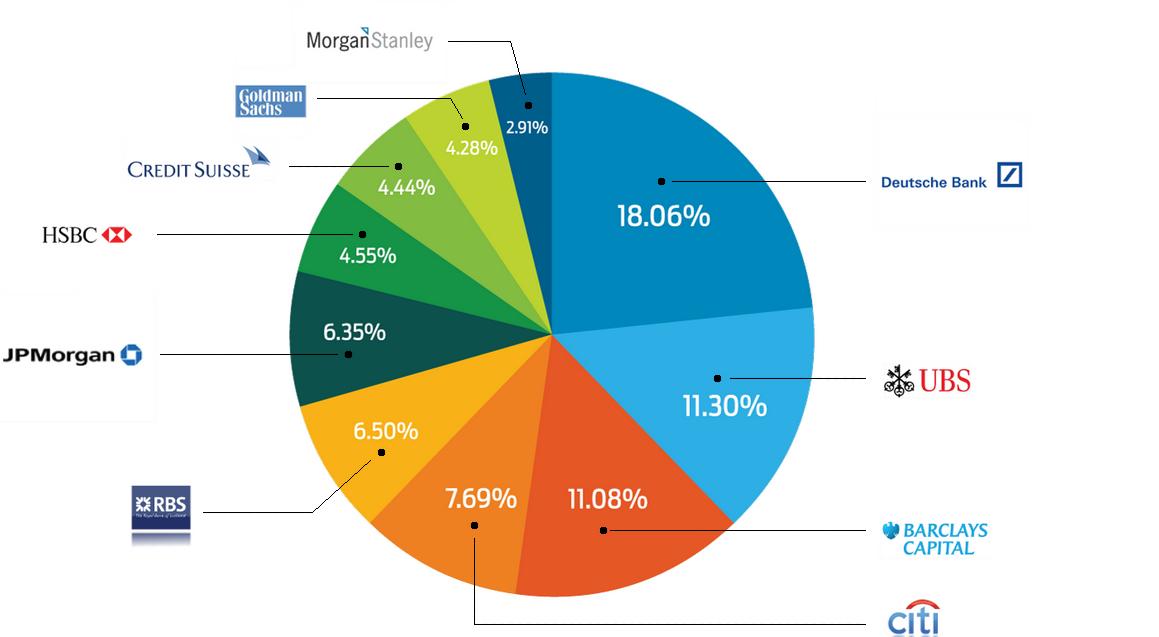
Banks. They handle Forex transactions in high volumes that often determine the future movements of financial markets. Currently, the five largest banks in the world hold almost 55% of the order volumes of the financial market. The minimum transaction in the interbank platforms is 10 million, the equivalent of 10 lots. Banks, of course, are trading without leverage, and utilize a variety of trading strategies from High Frequency Trading, latency trading, and arbitrage trading to long-term trading strategies.
The largest interbank platforms are EBS and Reuters and other interbank platforms are Integral, Currenex, Hotspot, Liquid-X, 360-T, and LavaFX.
Banks in the financial market make their biggest profits not from their own speculations, which are of course also a part of their portfolio, but from an execution of transactions for their worldwide corporate customers (car companies, technology companies, pharmaceutical companies, and all corporations that are doing business internationally).
Trades of corporate clients are executed according to the Reuters benchmark, which is the current market rate at 16:00 London time. Trillions of dollars in portfolios of money managers and investment funds are valued by this benchmark.
According to our information, bank traders on corporate transactions of 800 million USD thanks to his insider information about the transaction can earn up to an additional 2.5 million USD.
Other financial institutions – including investment funds, insurance companies, etc. They usually execute their transactions through a broker with institutional solutions or banks, and act in the financial market in order to ensure their risk management (hedging) and for speculation purposes (profit).